Artificial intelligence (AI) technology has emerged in the 21st century to transform industries, economies, and human daily lives. From self-driving cars to virtual assistants, AI is no longer a futuristic concept but a present reality. This article delves into the intricacies of AI, exploring its history, current applications, ethical considerations, and future potential. Stay tuned to kubecodes until the end of the blog.

The Evolution of Artificial Intelligence
The concept of Artificial intelligence dates back to ancient history, where myths and stories often depicted artificial beings endowed with intelligence. We can confidently say that the main foundation of artificial intelligence science was laid in the mid-20th century. The term “Artificial Intelligence” was coined by John McCarthy in 1956 during the Dartmouth Conference, which is considered the birth of AI as a field of study.
Early AI research focused on implementing symbolic methods and problem solving. Pioneers like Alan Turing, who proposed the Turing Test, and Marvin Minsky, who co-founded the MIT AI Lab, laid the groundwork for future advancements. The 1980s saw the emergence of systems designed to mimic human decision-making. Despite initial enthusiasm, progress was slow due to limited computational power and data availability.
The advent of the internet and the exponential growth of data in the 21st century catalyzed a new era of Artificial intelligence. Machine learning, a subset of AI, gained prominence, enabling computers to learn from data without explicit programming. The development of deep learning, powered by neural networks, further accelerated AI capabilities, leading to breakthroughs in image and speech recognition, natural language processing, and more.
Core Concepts of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence encompasses a variety of technologies and methods. At its core, AI aims to create systems that can perform tasks requiring human intelligence. These tasks include reasoning, learning, perception, problem-solving, and language understanding.
- Machine Learning (ML): ML is a subset of AI that focuses on developing algorithms that allow computers to learn from and make predictions based on data. Supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning are the primary types of ML.
- Deep Learning: A subset of ML, deep learning uses neural networks with many layers (hence “deep”) to model complex patterns in data. It has been instrumental in advancing fields like computer vision and natural language processing.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP technology enables machines to understand, interpret, and produce human language. Applications include bots, language translation, and sentiment analysis.
- Computer Vision: This field focuses on enabling machines to interpret and understand visual information from the world, such as images and videos. Facial recognition to self-driving vehicles fall into this category.
- Robotics: Artificial intelligence-driven robotics involves creating machines that can perform tasks autonomously or semi-autonomously. These robots are used in manufacturing, healthcare, and even space exploration.
Current Applications of AI
AI has permeated various sectors, revolutionizing traditional practices and creating new opportunities. Here are some notable applications:
- Healthcare: AI is transforming healthcare by improving diagnostics, personalizing treatment, and streamlining administrative tasks. Machine learning algorithms can analyze medical images to detect diseases like cancer with high accuracy. AI-powered chatbots assist in patient triage, while predictive analytics help in managing hospital resources.
- Finance: In the financial sector, Artificial intelligence technology is used to detect fraud, optimize algorithmic trading indicators, manage risk, and preserve capital. AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of transaction data to identify suspicious activities. Robo-advisors provide personalized investment advice, making financial planning more accessible.
- Retail: AI technology helps retailers create a better user experience through personalized recommendations, inventory management, and customer service. E-commerce platforms use AI to analyze user behavior and suggest products. Chatbots handle customer inquiries, while AI-driven logistics optimize supply chains.
- Transportation: Autonomous vehicles are one of the most prominent Artificial intelligence applications in transportation. Companies like Tesla and Waymo are developing self-driving cars that rely on AI for navigation and decision-making. AI also optimizes traffic management and route planning.
- Entertainment: AI is reshaping the entertainment industry by enabling content recommendation, creation, and distribution. Streaming services like Netflix use AI to suggest shows based on user preferences. AI-generated music and art are gaining traction, blurring the lines between human and machine creativity.
- Education: AI is personalizing education by adapting learning materials to individual students’ needs. Intelligent tutoring systems provide real-time feedback, while AI-driven analytics help educators identify at-risk students. Language learning apps use AI to enhance pronunciation and vocabulary acquisition.
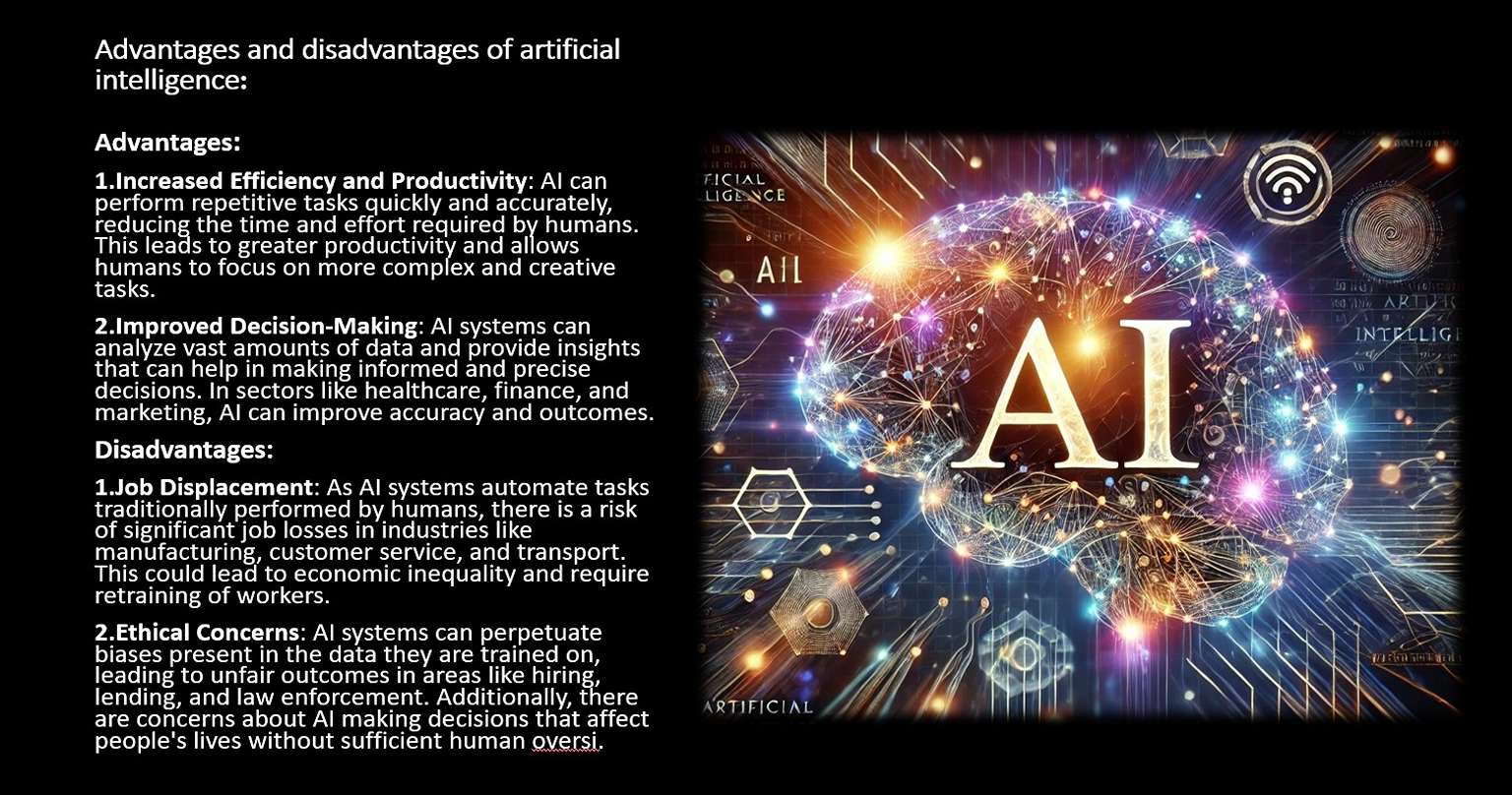
Ethical Considerations and Challenges
While AI offers immense potential, it also raises significant ethical and societal challenges. Addressing these concerns is crucial to ensuring that Artificial intelligence benefits humanity as a whole.
- Bias and Fairness: AI systems adapt to the data they are given. If the training data contains biases, the AI models can perpetuate and even amplify these biases. Such conditions can lead to unfair treatment in areas such as hiring, lending, and law enforcement. Ensuring fairness and transparency in AI algorithms is a pressing challenge.
- Privacy: AI systems often rely on vast amounts of personal data, raising concerns about privacy and data security. Unauthorized access to sensitive information will also have severe consequences. Striking a balance between data utilization and privacy protection is essential.
- Job Displacement: The automation of tasks through AI has the potential to displace jobs, particularly in routine and manual occupations. While AI can create new job opportunities, there is a need for reskilling and upskilling the workforce to adapt to the changing job landscape.
- Accountability: As Artificial intelligence systems make decisions that impact individuals and society, questions of accountability arise. Who is responsible when an AI system makes a wrong decision? Establishing clear guidelines and legal frameworks for AI accountability is crucial.
- Autonomous Weapons: The development of AI-powered autonomous weapons raises ethical and security concerns. The potential for misuse and the lack of human oversight in life-and-death decisions are contentious issues that require international regulation.
Application of Artificial Intelligence in Cryptocurrency
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a transformative force across various industries, and the cryptocurrency sector is no exception. The integration of AI in cryptocurrency is enhancing the efficiency, security, and functionality of digital currencies and blockchain technologies. Here are some key applications of AI in the cryptocurrency domain:
Market Analysis and Prediction
- Algorithmic Trading: AI-powered algorithms analyze vast amounts of historical and real-time market data to identify patterns and trends. These algorithms can execute trades at high speeds and with precision, often outperforming human traders.
- Sentiment Analysis: Artificial intelligence tools can scan social media, news, and other online platforms to gauge public sentiment about specific cryptocurrencies. This information can be used to predict market movements based on the collective mood of investors.
Fraud Detection and Security
- Anomaly Detection: AI systems can monitor blockchain transactions in real-time to detect unusual patterns that may indicate fraudulent activities, such as double-spending or unauthorized access.
- Enhanced Security Protocols: AI can be used to develop advanced cryptographic techniques and security protocols to protect digital wallets and exchanges from hacking attempts.
Smart Contracts
- Automated Execution: Artificial intelligence can enhance smart contracts by enabling them to execute automatically based on predefined conditions. This reduces the need for intermediaries and increases the efficiency of transactions.
- Adaptive Contracts: AI can make smart contracts more flexible by allowing them to adapt to changing conditions and inputs, making them more versatile and applicable to a wider range of scenarios.
Portfolio Management
- Robo-Advisors: AI-driven robo-advisors can manage cryptocurrency portfolios by analyzing market conditions and making investment decisions based on the user’s risk tolerance and financial goals.
- Risk Management: Artificial intelligence can assess the risk associated with various cryptocurrencies and suggest diversification strategies to minimize potential losses.
Blockchain Optimization
- Scalability Solutions: AI can help optimize blockchain networks by improving consensus algorithms and reducing the computational load, thereby enhancing scalability and transaction speed.
- Energy Efficiency: AI can be used to develop more energy-efficient mining processes, reducing the environmental impact of cryptocurrency mining.
Regulatory Compliance
- Automated Reporting: AI can automate the process of generating reports required by regulatory authorities, ensuring compliance with legal standards and reducing the administrative burden on cryptocurrency firms.
- KYC and AML: Artificial intelligence can streamline Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) processes by quickly verifying identities and detecting suspicious activities.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
- Lending and Borrowing: AI can optimize lending and borrowing platforms by assessing credit risk and setting interest rates dynamically based on market conditions.
Liquidity Provision: AI algorithms can manage liquidity pools in decentralized exchanges, ensuring that there is always enough liquidity for trading.
Customer Support
- Chatbots: AI-powered chatbots can provide 24/7 customer support, answering queries related to cryptocurrency transactions, wallet management, and more.
- Personalized Recommendations: AI can analyze user behavior and preferences to offer personalized investment advice and product recommendations.
Data Privacy
- Privacy-Preserving Techniques: AI can be used to develop advanced privacy-preserving techniques, such as zero-knowledge proofs, to enhance the confidentiality of blockchain transactions.
Research and Development
- Cryptographic Research: Artificial intelligence can assist in the development of new cryptographic algorithms and protocols, making blockchain networks more secure and efficient.
- Simulation and Testing: AI can simulate various blockchain scenarios to test the robustness and scalability of new protocols before they are deployed.
The Future of Artificial Intelligence
The future of artificial intelligence is very exciting, but it cannot be predicted exactly. As technology continues to evolve, AI is expected to become more integrated into our lives, driving innovation and solving complex problems. Here are some potential future developments:
- General AI: Current AI systems are designed for specific tasks (narrow AI). The pursuit of General Artificial intelligence, which can perform any intellectual task that a human can do, remains a long-term goal. Achieving General AI would require significant advancements in understanding human cognition and developing more sophisticated algorithms.
- AI and Human Collaboration: The future may see more collaborative interactions between humans and AI. AI systems could augment human capabilities, enabling us to solve problems more efficiently and creatively. This collaboration could extend to fields like scientific research, where AI assists in data analysis and hypothesis generation.
- Ethical AI: As AI becomes more pervasive, there will be a growing emphasis on developing ethical AI systems. This includes creating algorithms that are transparent, fair, and accountable. Ethical AI frameworks will be essential in guiding the responsible development and deployment of AI technologies.
- AI in Space Exploration: AI has the potential to revolutionize space exploration by enabling autonomous spacecraft and rovers. AI-driven systems can analyze vast amounts of data from space missions, identify patterns, and make real-time decisions. This could accelerate our understanding of the universe and the search for extraterrestrial life.
- AI and Climate Change: AI can play a crucial role in addressing climate change by optimizing energy consumption, predicting environmental changes, and developing sustainable solutions. AI-driven models can analyze climate data to inform policy decisions and mitigate the impact of global warming.

Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is a powerful tool that is reshaping the world as we know it. Its applications span across industries, offering solutions to some of the most pressing challenges of our time. However, the rapid advancement of AI also brings ethical and societal considerations that must be addressed to ensure its benefits are realized equitably.
As we move forward, the collaboration between technologists, policymakers, and society at large will be crucial in shaping the future of AI. By fostering innovation while upholding ethical standards, we can harness the potential of AI to create a better, more intelligent world. The journey of AI is just beginning, and its impact on
humanity will undoubtedly be profound.